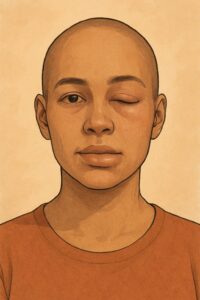
Autoimmune angioedema is a rare condition where the immune system mistakenly triggers swelling in the deeper layers of the skin or mucous membranes—like the face, lips, tongue, throat, hands, or digestive tract. This swelling can be unpredictable and scary, especially if it affects breathing or causes stomach pain.
In autoimmune angioedema, the immune system may interfere with a protein called C1 inhibitor, leading to abnormal activation of the body’s inflammatory pathways.