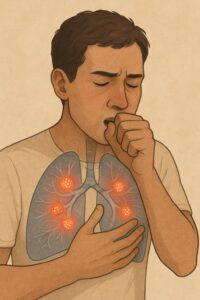
Sarcoidosis is a chronic inflammatory disease where the body forms small clusters of immune cells called granulomas in various organs. These granulomas can interfere with organ function and cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on where they form.
The lungs and lymph nodes are most commonly affected, but sarcoidosis can involve the skin, eyes, heart, liver, brain, and other organs. It’s considered an immune-mediated disease and is sometimes classified as autoimmune, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood.